The Irony of Smoking to Stay Thin: Smoking Increases Belly Fat
The worry of gaining weight is a common excuse for smokers not to quit. A study published in the scientific journal Addiction has found that both starting smoking and lifetime smoking may increase abdominal fat, especially visceral fat – the unhealthy fat deep inside the abdomen that is linked to a higher risk of heart disease, diabetes, stroke, and dementia.

Smokers tend to have lower body weights than non-smokers, but they also have more abdominal fat, and more abdominal visceral fat. Visceral fat is hard to see; you can have a flat stomach and still have unhealthy amounts of it, raising your risk of serious illness. This new study in the journal Addiction offers supportive evidence that smoking may cause that type of fat to increase.
Researchers at the NNF Center for Basic Metabolic Research (CBMR), University of Copenhagen used a form of statistical analysis called Mendelian randomization (MR) to determine whether smoking causes an increase in abdominal fat. MR combines the results from different genetic studies to look for causal relationships between an exposure (in this case, smoking) and outcome (increased abdominal fat). This new study combined multiple genetic results from European ancestry studies of smoking exposures and measures of body fat distribution (e.g., waist-hip ratio and waist and hip circumferences).
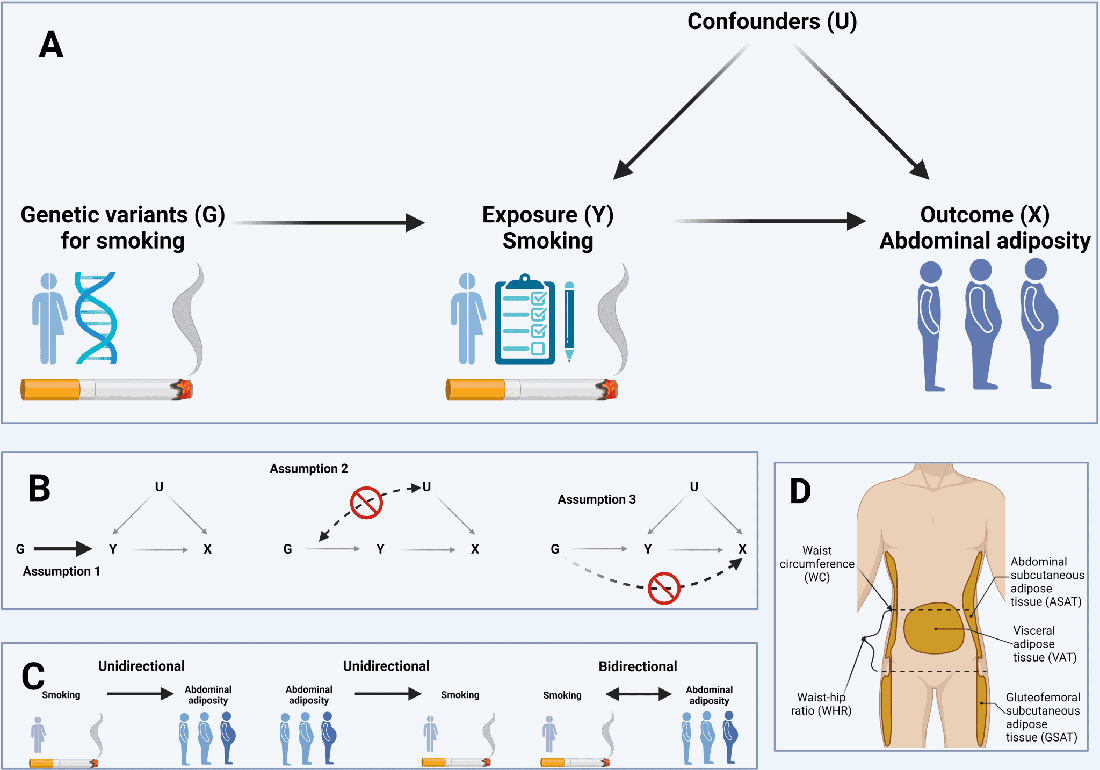
First, the researchers used previous genetic studies to identify which genes are linked to smoking habits and body fat distribution. Second, they used this genetic information to determine whether people with genes associated with smoking tend to have different body fat distributions. Finally, they accounted for other influences, such as alcohol consumption or socioeconomic background, to ensure that any connections they found between smoking and body fat distribution were truly due to smoking itself and not other factors.

Lead author Assistant Professor Germán D. Carrasquilla (Kilpeläinen Group) explains: “This study found that starting to smoke and smoking over a lifetime might cause an increase in belly fat, as seen by measurements of waist-to-hip ratio. In a further analysis, we also found that the type of fat that increases is more likely the visceral fat, rather than the fat just under the skin.”
Germán adds that previous studies have been prone to confounding, which happens when an independent variable affects the results. Because they adopted a study design using genetic variations, it does a better job of reducing or controlling for those variables. The influence of smoking on belly fat seems to happen regardless of other factors such as socioeconomic status, alcohol use, ADHD, or how much of a risk-taker someone is.
“From a public health point of view, these findings reinforce the importance of large-scale efforts to prevent and reduce smoking in the general population, as this may also help to reduce abdominal visceral fat and all the chronic diseases that are related to it. Reducing one major health risk in the population will, indirectly, reduce another major health risk.”.
The researchers determined that excess abdominal fat in smokers was predominantly visceral fat by studying how DNA variants linked to smoking habits and belly fat relate to fat compartments in different parts of the body. The key finding is that these genetic factors are more strongly linked to increased visceral adipose tissue—the deep fat that wraps around the abdominal organs—than to subcutaneous fat that is stored under the skin.
The two underlying European ancestry studies were large in scale: the smoking study looked at 1.2 million people who started smoking and over 450,000 lifetime smokers, and the body fat distribution study included over 600,000 people.
Altmetrics
Contact
Assistant Germán D. Carrasquilla
german.carrasquilla@sund.ku.dk
Associate Professor Tuomas O. Kilpeläinen
tuomas.kilpelainen@sund.ku.dk
