Signaling Pathways in the Functions of Adipocytes in the Emanuelli Group
The Emanuelli Group investigates the complex nature of the signaling networks involved in the endocrine control of metabolic functions, with a special focus on defining the signals and molecular pathways that orchestrate the functions of adipocytes in metabolic health and disease.

The adipose tissue is critically contributing to the regulation of energy balance via its energy storing or dissipating capacities, and via endocrine signaling.
Combining high throughput and unbiased approaches, with functional interrogation via CRISPR-mediated gene editing and manipulation in cells and animals, the focus of the Emanuelli Group is to dissect the molecular mechanisms controlling the functions of white, brown and beige fat cells and orchestrating the remarkable adaptive responses of these cells to metabolic challenges.
Brice Emanuelli explains: “Recognizing the factors optimizing or dysregulating the adipose metabolic and adaptive processes holds promise in offering novel strategies to combat obesity and associated cardiometabolic disorders.”
“Afadin is a scaffold protein repressing insulin action via HDAC6 in adipose tissue”
Published in EMBO Reports in 2019 this study shows that the scaffold protein Afadin dampens insulin action in adipocytes and impairs adipose tissue function by a negative feedback mechanism involving Afadin phosphorylation, recruitment of HDAC6 and suppression of the insulin signaling pathway.
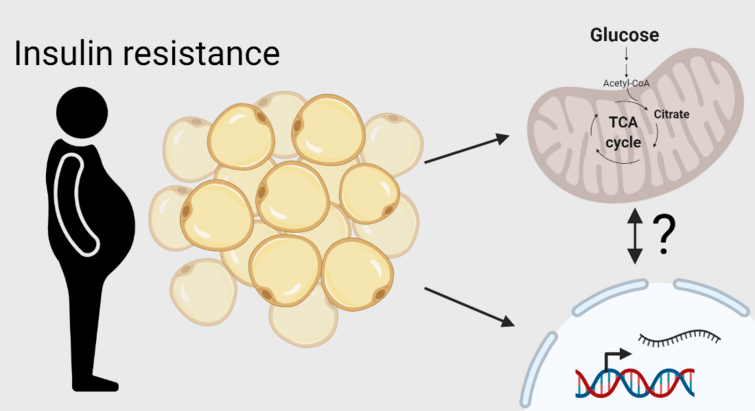
"Insulin resistance rewires the metabolic gene program and glucose utilization in human white adipocytes"
In this study published in International Journal of Obesity in 2022 we characterized the transcriptional alterations associated with insulin resistance in human visceral fat and uncovered a metabolic rewiring of glucose fate in human adipocytes that may contribute to adipose dysfunction associated with obesity.
“White adipose remodeling during browning in mice involves YBX1 to drive thermogenic commitment”
In this work published in Molecular Metabolism in 2021, we delineated the temporal proteomic changes occurring during the cold-stimulated browning of white adipose tissue in mice. We found that a core of transcriptional regulators was acutely induced. Among those, our findings further revealed the role of the cold-shock domain containing protein YBX1 as a novel factor impacting the adipogenic fate toward the thermogenic lineage.
Funding sources for our group include the Novo Nordisk Foundation, The Danish Diabetes Academy, the Copenhagen Bioscience PhD Programme and the European Foundation for the Study of Diabetes.
News

Staff list
| Name | Title | Phone | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Avramets, Diana | PhD Fellow | +4535329174 | |
| Emanuelli, Brice | Associate Professor | +4535337016 | |
| Jacobsen, Ida Marie Boi | Postdoc | +4535333518 | |
| Sönmeztekin, Dilara | Erasmus Master Student |



